Blog
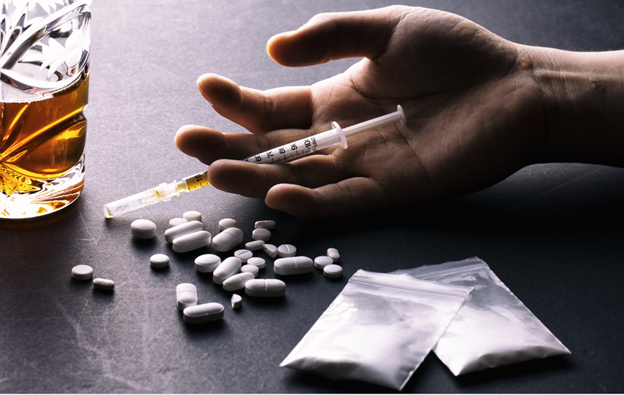
What Do Drugs Do to Your Brain?

Recent Posts
Prescription Drug Abuse: Everything You Need to Know
Various health conditions call for prescription medication. Unfortunately, some prescription drugs are misused leading to…
1 month ago
The Reality of High-functioning Alcoholism: What You Need to Know
The accessibility of alcohol and its being widely accepted as a social lubricant contribute to…
1 month ago
Understanding Aftercare: Key Programs for Lasting Addiction Recovery
After you’ve completed a primary treatment program for SUD, the next step is just as…
1 month ago
12-Step Program Explained: Key Principles & Benefits
Although initially developed to help individuals overcome alcoholism, the Alcoholics Anonymous 12-step program has since…
1 month ago
How Anonymous is an Outpatient Drug Rehab Center?
If you’re considering outpatient drug rehab, you’re probably wondering: how anonymous is it really? Can…
1 month ago
How Drugs Affect the Body
Drugs—whether prescription, recreational, or illicit—affect nearly every system in your body, sometimes in ways that…
1 month ago